Agentic AI: The Rise of Intelligent Agents and Virtual AI Systems
Jul 21, 2025
As artificial intelligence continues to mature, the idea of Agentic AI is emerging as one of its most transformative frontiers. But what exactly is Agentic AI? In essence, Agentic AI refers to a new class of AI systems capable of operating with a high degree of autonomy, making decisions, taking actions, and often learning from their environment to achieve specific goals. Unlike traditional AI that might perform a single, pre-defined task, Agentic AI systems—or intelligent agents—can chain together multiple actions, adapt to new information, and pursue objectives proactively, much like a human agent would.
In 2025, Agentic AI is at the heart of the next generation of automation: intelligent agents embedded across workflows, business systems, and customer touchpoints to amplify human productivity and drive fully autonomous business operations. Whether it’s a pipeline review agent, a conversational AI agent integrated into your CRM, or a multi-agent system orchestrating complex workflows — Agentic AI is shaping how we work, interact, and make decisions.
What are AI Agents?
In simple terms, an AI agent is an autonomous entity that observes its environment through various inputs (e.g., CRM data, email interactions, public company news) and acts upon that environment using various outputs (e.g., sending an email, updating a deal stage, scheduling a meeting) and directs its activity toward achieving specific objectives. It's a conceptual framework that helps us design AI systems capable of rational behavior in dynamic sales environments.
Key Properties of AI Agents
Autonomy: This is perhaps the most defining characteristic. An intelligent agent operates independently, without constant human intervention. It can make its own decisions and initiate actions based on its internal goals and perception of the environment. This means it doesn't just wait for instructions; it actively pursues its objectives.
Reactivity: An intelligent agent is responsive to its environment. It can perceive changes and react to them in a timely and appropriate manner. If new information becomes available, or if the environment shifts, the agent can adjust its behavior accordingly.
Proactiveness: Beyond merely reacting, an intelligent agent can initiate goal-directed behavior. It doesn't just wait for events to happen; it takes initiative to achieve its objectives, often anticipating future states or requirements. This involves planning and foresight.
Social Ability: Many modern intelligent agents possess the ability to interact with other agents (both human and AI). This could involve communication, negotiation, or collaboration to achieve shared or individual goals. This property is crucial for the development of multi-agent systems and collaborative AI workflows.
Understanding these properties is crucial to appreciating the power and potential of an agent in artificial intelligence. They are the building blocks for the more complex agentic AI systems we see emerging today.
From Virtual Assistants to AI Agents: The Evolution
To understand Agentic AI’s promise, it helps to look at how we got here.
The early days of AI in business brought AI-powered virtual assistants — simple bots that answered FAQs, handled routine tasks, or guided website visitors. These virtual agents followed pre-set scripts and decision trees with limited flexibility. Next came virtual agents that leveraged natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to handle more dynamic, conversational interactions. A virtual agent could handle tier-one support or basic scheduling but still lacked true task-level autonomy.
Modern AI Agents take the virtual assistant concept to the next level. Unlike static bots, AI agents are task-aware, context-rich, and capable of chaining multiple actions together. For example, an AI-powered virtual agent in a B2B setting might do more than just surface CRM data — it could review deal health, summarize call transcripts, and draft follow-up emails for reps to send, all autonomously.
While terms like "virtual assistant" and "AI agent" are often used interchangeably, there are critical distinctions that highlight the significant evolution in AI capabilities.
Aspect | AI-Powered Bots | Virtual Agents | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|---|
Definition | Script-driven programs for simple, repetitive tasks | Conversational AI systems with broader capabilities | Autonomous systems with goal-directed behavior |
Core Function | Automate predefined tasks using rule-based scripts | Understand and respond to natural language queries | Plan, decide, and execute complex tasks independently |
Level of Intelligence | Basic — limited to scripted interactions | Moderate — understands intent, integrates with services | Advanced — autonomous decision-making, planning, learning |
Examples | FAQ chatbots, website pop-ups | Siri, Alexa, customer service bots | Self-driving agents, multi-step virtual sales assistants, autonomous research agents |
Interaction Style | Pre-programmed responses | Dynamic conversations with contextual understanding | Proactive actions, collaboration, self-learning |
Learning Capability | Static — no learning beyond scripts | Some learning through machine learning models | Continuous learning from environment and feedback |
Autonomy | None — fully reactive to specific triggers | Limited — reacts to user prompts | High — sets and achieves goals without explicit step-by-step input |
Primary Use Cases | Redirecting users, answering basic FAQs | Voice assistants, customer support, scheduling | Complex decision support, autonomous workflows, multi-step goal completion |
Proactivity | Not proactive | Slightly proactive (e.g., reminders) | Highly proactive — plans and initiates actions to achieve objectives |
How AI Agents Are More Autonomous and Task-Aware
The increased autonomy and task awareness of AI Agent systems stem from several advancements:
Goal-Oriented Reasoning: Unlike previous iterations that were primarily driven by immediate prompts, intelligent agents are designed with explicit goals in mind. They can break down these high-level goals into sub-goals and then plan the necessary steps to achieve them.
Dynamic Planning and Re-planning: If an obstacle arises or the environment changes, an AI agent can dynamically re-plan its approach. This adaptability is crucial for operating in real-world, unpredictable scenarios.
Tool Use and Integration: Modern AI agents can effectively "use" external tools and APIs. This means they aren't limited to their internal capabilities but can leverage a vast ecosystem of software applications, databases, and web services to accomplish tasks. For example, an ai powered virtual agent might use a CRM to pull customer data, then a scheduling tool to book an appointment, and finally a communication platform to send a confirmation.
Memory and Context Retention: Intelligent virtual agents maintain context over longer interactions and can learn from past experiences, allowing them to refine their strategies and improve performance over time. This persistent memory is vital for complex, multi-stage tasks.
This evolution signifies a move from AI as a tool for specific tasks to AI as a proactive partner, capable of orchestrating complex workflows and making intelligent decisions independently.
Conversational AI Agents and Their Role in B2B Workflows
One of the most visible forms of Agentic AI today is the conversational AI agent. Unlike basic chatbots, conversational agents understand context, maintain memory, and can handle nuanced tasks across departments.
Where Conversational AI Agents Deliver Value:
Revenue Operations (RevOps)
Conversational agents help sales leaders review pipelines, flag deal risks, and recommend next steps — all by querying systems in natural language. A manager might ask, “Show me all Q3 deals slipping by more than two stages,” and the agent fetches data, applies logic, and surfaces insights.Customer Support
Instead of routing customers to static FAQ bots, conversational AI agents resolve multi-step issues, escalate cases, and summarize interactions for human agents to take over seamlessly.Forecasting and Analytics
Conversational AI agents are becoming trusted copilots for revenue forecasting — pulling CRM data, analyzing trends, and generating updates on the fly.
In all these examples, the AI intelligent agent doesn’t just answer — it reasons, generates context, and coordinates across tools.
Autonomous AI Agents: Capabilities and Use Cases
Autonomous AI takes Agentic AI even further. These agents act independently to execute tasks, learn from feedback, and chain actions in complex workflows with minimal human intervention.
Key Capabilities:
Task Automation: Automate repetitive processes like meeting scheduling, opportunity updates, or quote generation.
Multi-step Decision-Making: Agents can reason through ambiguous scenarios — like whether to escalate a risky deal or update forecast numbers automatically.
Cross-Tool Orchestration: Modern AI agents can integrate with CRMs, calendars, email clients, and third-party data sources.
Dynamic Task Decomposition: Given a high-level goal, an autonomous agent can break it down into a series of smaller, manageable sub-tasks. It can then determine the optimal sequence for these tasks.
Self-Correction and Adaptation: If a step fails or the environment changes, the agent doesn't simply stop. It can identify the issue, re-evaluate its plan, and attempt alternative approaches to achieve its objective.
Complex Reasoning and Planning: Autonomous agents employ sophisticated reasoning modules to navigate ambiguous situations, evaluate potential outcomes, and make decisions that align with their goals. This often involves chaining together various AI models (e.g., generative AI for content creation, analytical AI for data processing).
Continuous Learning: Many autonomous agents are designed to learn from their experiences, refining their strategies and improving their performance over time. This can involve reinforcement learning or other adaptive mechanisms.
Examples in B2B SaaS
Pipeline Review Agents: Automatically scan opportunities, detect stale deals, and notify reps.
Meeting Summarizers: Listen to calls, extract key points, and draft follow-ups.
Quarterly Business Review (QBR) Bots: Gather sales data, build slides, and provide recommendations for account managers.
All these scenarios show how autonomous AI is redefining how businesses handle tasks that once required entire teams.
The Architecture Behind Agentic AI Systems
So, how do these Agentic AI systems actually work under the hood?
At their core, AI agents rely on an agent-environment interaction loop: the agent perceives its environment (e.g., via APIs, data streams), reasons about the state, decides on an action, and executes that action.
Key Building Blocks:
Perception Layer: Ingests data — from CRM records, conversations, or external APIs.
Reasoning Module: Uses large language models (LLMs) and symbolic reasoning to plan next steps.
Task Planners: Break larger tasks into sub-tasks and coordinate execution.
Action Layer: Executes tasks autonomously by calling other systems or prompting humans.
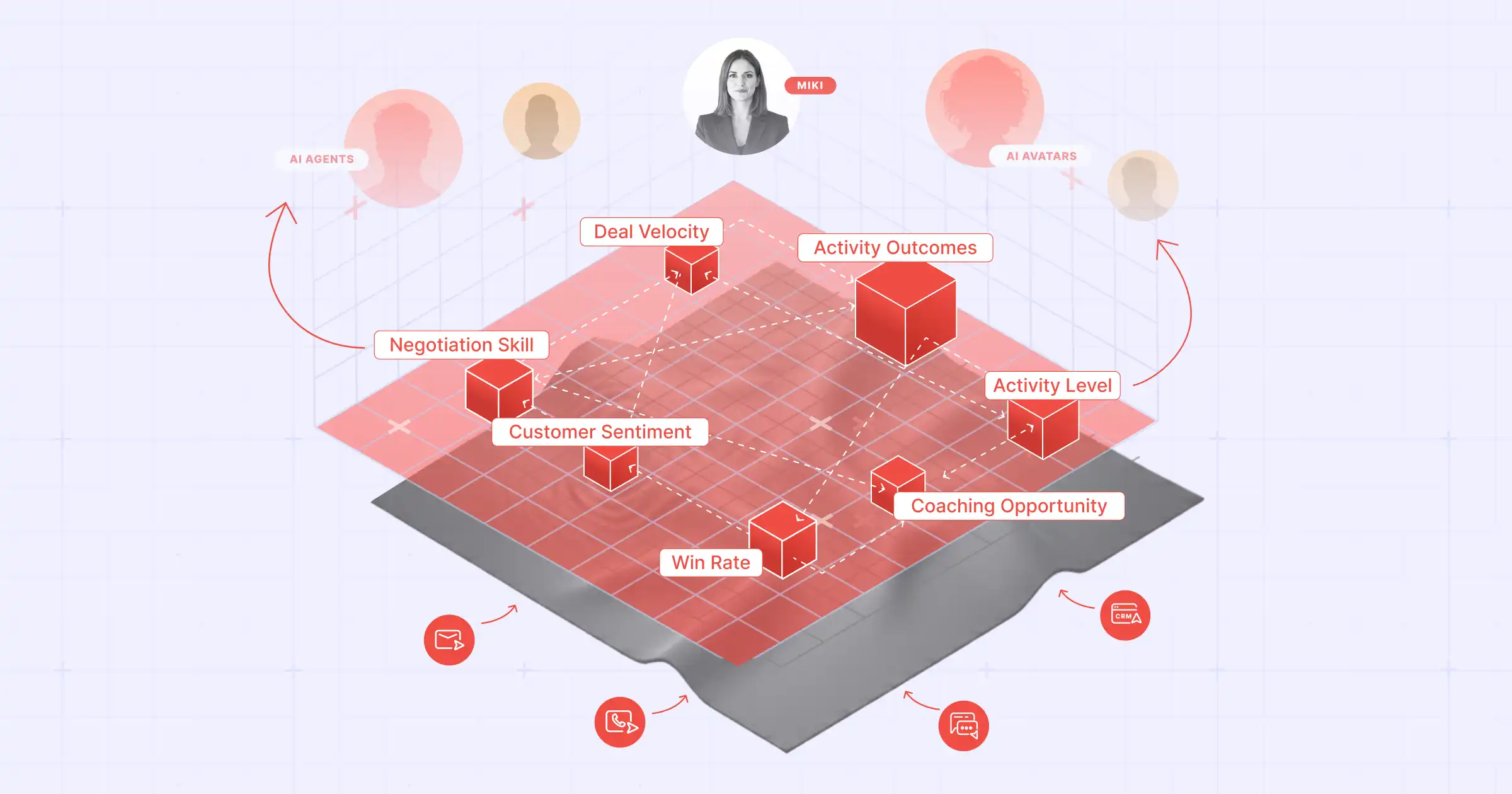
MIKI, Aviso’s Agentic AI Chief of Staff, exemplifies this architecture by leveraging advanced reasoning modules and proprietary task planners to orchestrate complex RevOps workflows. It seamlessly integrates with enterprise CRMs and sales systems, using a dynamic memory to ensure contextually aware decision-making throughout the revenue lifecycle. MIKI's ability to autonomously identify sales blockers, orchestrate cross-agent actions, drive QBRs, surface risks with next steps, and generate earnings insights showcases the power of a fully integrated agentic AI system.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While Agentic AI holds immense promise, it also raises unique challenges:
Hallucination: Like other LLMs, agents can generate inaccurate information. In autonomous workflows, this can lead to bad decisions at scale.
Data Leakage: Agents must handle sensitive business data carefully to prevent accidental leaks.
Lack of Explainability: It’s not always clear why an agent made a particular decision. This black-box nature complicates auditing and trust.
Accountability: Who is responsible when an agent’s autonomous decision goes wrong? Organizations need clear guardrails and oversight.
Solving these challenges requires robust testing, human-in-the-loop controls, clear audit trails, and accountability frameworks.
What’s Next? Agentic AI in the Enterprise
For B2B enterprises, adopting Agentic AI means faster execution, richer insights, and a path toward fully autonomous, data-driven operations.
The future of Agentic AI lies in creating collaborative agent networks. Instead of a single AI agent performing a task, we’ll need multi-agent orchestration — clusters of specialized agents that plan, communicate, and execute together.
Imagine a revenue team deploying an entire ecosystem of agents:
One agent analyzes pipeline health.
Another preps QBR slides.
A third coordinates follow-ups with the customer.
All while feeding insights back into core CRM systems.
Platforms like Aviso are paving the way for this next leap.
Aviso’s Agentic AI isn’t just another AI assistant; it’s a fully orchestrated network of role-specific, task-driven agents that transform every layer of your GTM motion with autonomy, orchestration, context, trust, and enterprise scale.
Final Thoughts: Agentic AI Is Here — Are You Ready?
Agentic AI represents a paradigm shift that moves beyond the reactive nature of previous AI iterations. These intelligent agent systems, whether conversational or fully autonomous, are becoming proactive partners in driving business outcomes, from optimizing revenue operations and enhancing customer support to providing unprecedented levels of strategic insight. While challenges such as hallucination, data leakage, and the need for explainability remain, proactive development of guardrails and ethical frameworks is paving the way for responsible and impactful deployment.
The question is no longer if agentic AI will transform your enterprise, but when and how you will leverage its power. Businesses that embrace this new wave of intelligent automation will be best positioned to unlock significant efficiencies, gain competitive advantages, and navigate the complexities of the modern digital landscape.
Are you ready to embrace the rise of intelligent agents and virtual AI systems? The future of work is not just AI-powered; it's agent-orchestrated.
Ready to experience the shift? Book a demo or download our latest guide to see how Aviso’s Agentic AI solutions can help you unlock the power of intelligent agents in your revenue workflows.
FAQ
What is Agentic AI and why does it matter?
Agentic AI refers to AI systems that act as intelligent agents — perceiving their environment, reasoning, and taking actions autonomously. It matters because it unlocks new levels of automation, efficiency, and proactive decision-making that traditional passive AI cannot deliver.How is Agentic AI different from generative or conversational AI?
Generative AI creates content (text, images, code). Conversational AI interacts with humans through dialogue. Agentic AI combines these with reasoning and action capabilities, so agents not only generate or converse but also plan and execute tasks autonomously.What are the key capabilities of an intelligent agent?
Core capabilities include autonomy, reactivity to environmental changes, proactiveness to plan ahead, and social ability to interact with humans or other agents.Are conversational AI agents the same as intelligent agents?
Not exactly. All conversational AI agents are intelligent agents if they have reasoning and decision-making capabilities, but not all intelligent agents need to be conversational. Some operate silently in the background, orchestrating tasks and data flows.